Introduction
The world is transitioning toward sustainable energy sources to combat climate change, and solar energy stands at the forefront of this movement. One critical factor in determining the viability of solar energy systems is the solar irradiance index — a measure of the amount of solar power received per unit area at a location. Different countries experience vastly different levels of solar irradiance, influencing their solar energy potential, investment decisions, and renewable energy strategies.
This essay explores what the solar irradiance index is, why it matters, and how it varies from country to country.
Understanding Solar Irradiance Index
-
Definition: Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (usually measured in watts per square meter, W/m²) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
-
Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI): The most common measurement, representing total solar radiation received on a horizontal surface.
-
Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI): Measures the amount of solar radiation received per unit area by a surface that is always held perpendicular to the incoming rays.
-
Diffuse Horizontal Irradiance (DHI): Refers to sunlight scattered by the atmosphere and received from all directions.
Solar Irradiance Index varies based on:
-
Geographic latitude
-
Climate conditions (cloud cover, air pollution)
-
Seasonality (length of day and sun angle)
-
Altitude and landscape (mountains, sea level)
Importance of Solar Irradiance Index
-
Energy Production Estimation: Predicts how much electricity a solar system can generate.
-
Investment Decisions: Helps in siting solar farms and determining economic feasibility.
-
Policy Formulation: Aids governments in designing energy policies and subsidy programs.
-
Technological Adaptation: Different irradiance levels might dictate the types of solar panels or technologies used.
Global Solar Irradiance Distribution
The solar belt — regions between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn — receives the highest levels of solar irradiance. However, some countries outside the tropics also have strong solar potential due to clear skies and desert climates.
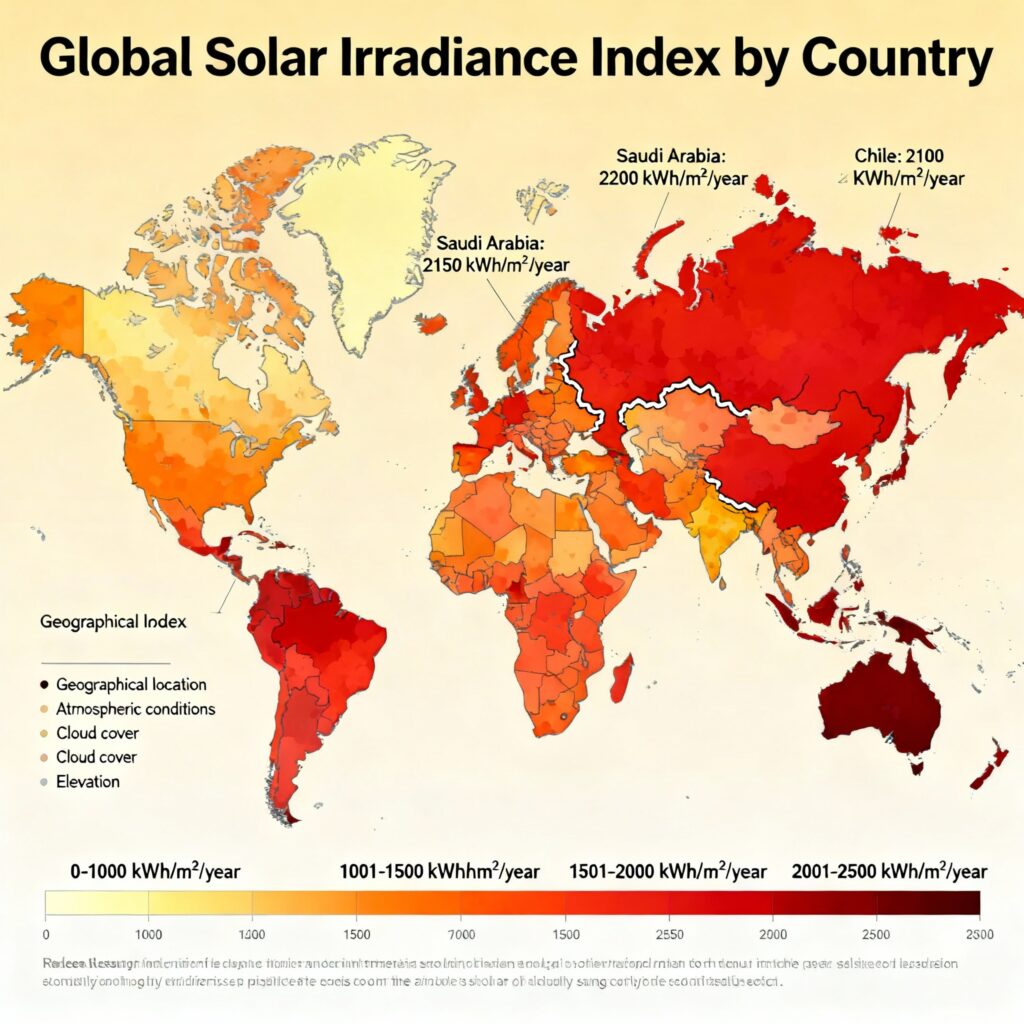
Solar Irradiance Index by Country (Average GHI Values)
Here’s a country-wise breakdown of average solar irradiance levels, measured in kWh/m²/day:
1. Chile
-
Average GHI: 6.0 – 7.5 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Atacama Desert — one of the sunniest places on Earth.
-
Remark: Chile is investing heavily in solar power, especially in the north.
2. Australia
-
Average GHI: 5.5 – 7.0 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Northern Territory and Queensland.
-
Remark: Australia has some of the highest rooftop solar adoption rates globally.
3. Saudi Arabia
-
Average GHI: 5.5 – 6.5 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Rub’ al Khali desert.
-
Remark: Major government initiatives like the “Vision 2030” focus heavily on solar energy.
4. United States (Southwest)
-
Average GHI: 5.0 – 6.5 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Arizona, Nevada, and New Mexico.
-
Remark: Home to some of the world’s largest solar power plants.
5. Egypt
-
Average GHI: 5.5 – 6.0 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Western Desert and Upper Egypt.
-
Remark: Egypt’s Benban Solar Park is among the largest globally.
6. India
-
Average GHI: 4.5 – 5.5 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Rajasthan, Gujarat.
-
Remark: India’s ambitious “National Solar Mission” aims for 500 GW renewable capacity by 2030.
7. Mexico
-
Average GHI: 5.0 – 6.5 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Sonoran Desert.
-
Remark: Mexico is a leader in solar energy in Latin America.
8. South Africa
-
Average GHI: 4.5 – 6.0 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Northern Cape Province.
-
Remark: The country has vast potential and growing solar projects.
9. Spain
-
Average GHI: 4.0 – 5.5 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Andalusia, Extremadura.
-
Remark: Spain was an early pioneer in solar power, especially concentrated solar power (CSP).
10. United Arab Emirates
-
Average GHI: 5.5 – 6.0 kWh/m²/day
-
Key Region: Abu Dhabi and Dubai.
-
Remark: Home to some of the world’s largest solar parks, like Noor Abu Dhabi.
Other Notable Countries
-
Morocco: 5.5–6.0 kWh/m²/day (Noor Solar Complex).
-
Brazil (Northeast): 5.0–6.0 kWh/m²/day.
-
Peru: 5.0–6.5 kWh/m²/day.
-
Israel: 5.0–6.0 kWh/m²/day.
-
Algeria: 5.0–6.5 kWh/m²/day.
Factors Affecting Solar Irradiance Beyond Geography
-
Altitude: Higher altitudes often receive more intense solar radiation.
-
Humidity: High moisture can reduce solar irradiance.
-
Aerosols and Pollution: Areas with high air pollution (e.g., parts of India, China) experience lower irradiance.
-
Snow Cover: Reflective surfaces can sometimes enhance photovoltaic efficiency slightly.
Global Patterns and Trends
-
Desert Regions: Offer the highest solar irradiance (e.g., Sahara, Sonoran, Atacama Deserts).
-
Urban vs Rural: Rural regions often have better solar resources due to lower pollution and less shading.
-
Tropical Rain Zones: Despite proximity to the equator, heavy cloud cover can lower actual available irradiance (e.g., parts of Indonesia, Congo).
Solar Energy Policy Tied to Irradiance
Countries with high solar irradiance are:
-
Launching large-scale solar farms (e.g., UAE’s Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park).
-
Offering feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and incentives to encourage residential and commercial solar adoption.
-
Developing off-grid solar solutions for rural and remote areas.
Future Implications
-
Solar Energy as a Primary Source: Many countries in the solar belt are positioning themselves to become energy exporters via hydrogen production powered by solar.
-
Energy Equity: High-irradiance but economically developing nations (like Ethiopia, Sudan) could leapfrog directly to clean energy if investments are made.
-
Climate Resilience: Solar energy helps build more climate-resilient infrastructure by reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Conclusion
Solar irradiance is a fundamental measure of a country’s solar energy potential. While natural geographic and climatic factors play a big role, human policy decisions, technological innovation, and financial investments determine how effectively a country can harness this clean, limitless resource. Countries like Chile, Australia, Saudi Arabia, and India exemplify regions that are maximizing their solar potential to transform their energy economies. As solar technology becomes cheaper and more efficient, and as global urgency around climate action grows, leveraging the solar irradiance index will become even more critical for sustainable development.