The Energy Performance Index (EPI) in a Building?
A Comprehensive Guide to Building Energy Efficiency
The Energy Performance Index (EPI) is a crucial metric used to assess the energy efficiency of buildings. Whether you’re targeting green certification, reducing operational costs, or complying with building codes, understanding EPI can significantly improve your sustainability efforts.
What is the Energy Performance Index (EPI)?
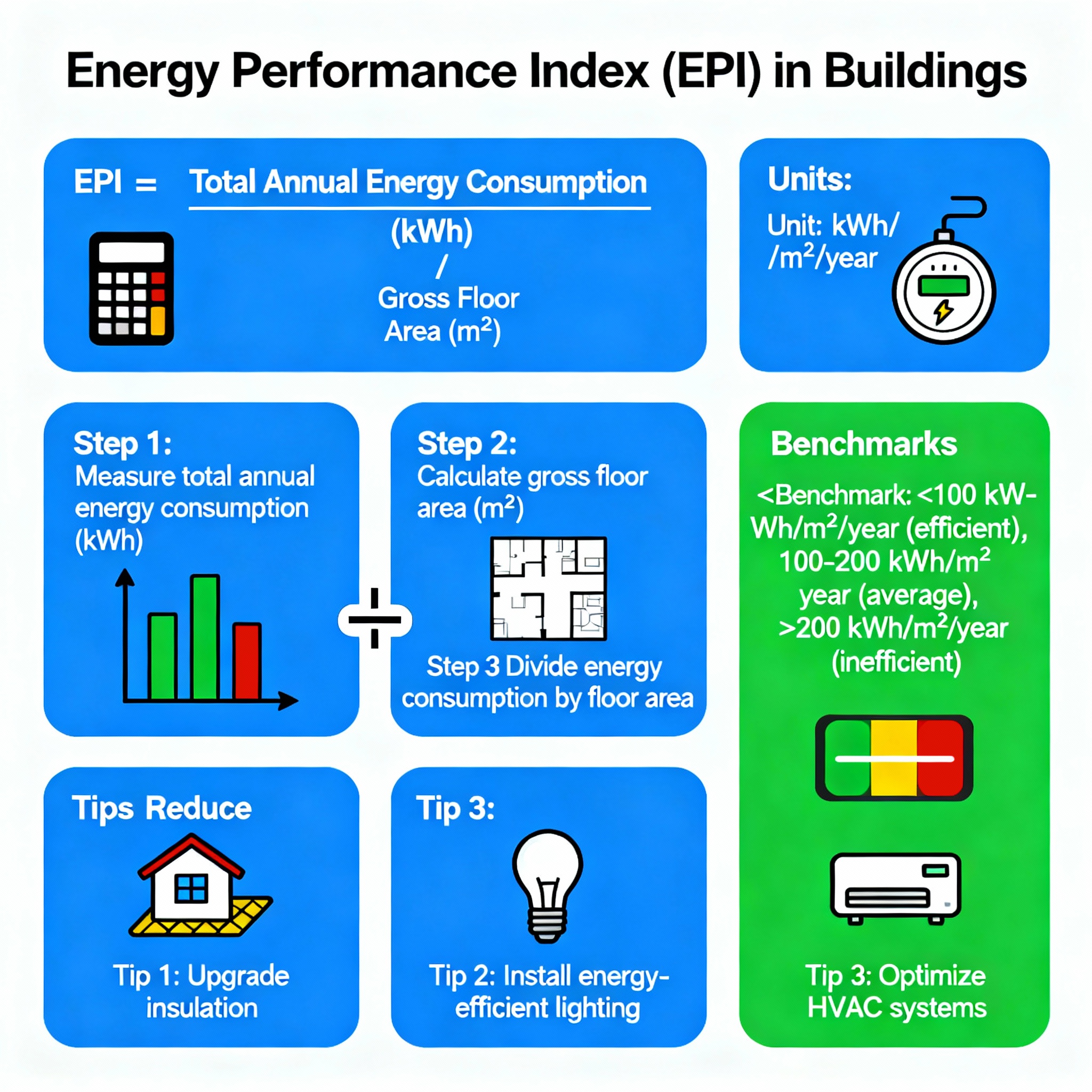
The Energy Performance Index is defined as the ratio of the total energy consumed by a building annually to its total built-up area. This index helps benchmark energy efficiency across various types of buildings, including commercial buildings, residential complexes, hospitals, and office spaces.
Formula:
EPI = Total Annual Energy Consumption (in kWh) / Total Built-up Area (in m²)
🟢 Want to learn how to calculate your EPI? Visit Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) for calculation tools and benchmarks.
Units of Measurement for EPI
The Energy Performance Index is commonly measured in:
-
kWh/m²/year – Kilowatt-hours per square meter per year
-
kWh/person/year – Kilowatt-hours per person per year (used in high-occupancy buildings like schools and hospitals)
Purpose of the Energy Performance Index
The EPI serves several important purposes:
-
✅ Benchmark energy performance across buildings
-
✅ Identify opportunities for energy efficiency upgrades
-
✅ Ensure compliance with energy codes like the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) in India
-
✅ Monitor post-retrofit energy savings
How is the Energy Performance Index Calculated?
To calculate a building’s EPI, total annual energy consumption (in kilowatt-hours) from electricity, fuel, and HVAC systems is divided by the total built-up area in square meters. Note that non-conditioned areas such as basements, parking zones, roads, and lawns are excluded from the calculation.
Learn more about calculating EPI using simulation software at EnergyPlus and OpenStudio.
Interpreting the Energy Performance Index
-
🔵 Lower EPI values = Higher energy efficiency
-
🔴 Higher EPI values = Greater energy consumption and lower efficiency
Benchmark your building’s EPI against national averages with tools from the US Department of Energy or India’s BEE STAR Rating Program.
EPI and Building Code Compliance
Building codes like the ECBC (India) and ASHRAE Standards (USA) set maximum allowable EPI values for different building categories and climate zones. Compliance can be achieved through:
1. Prescriptive Method
Adhering to standard design specs for:
-
Building envelope
-
Lighting systems
-
HVAC efficiency
2. Whole Building Performance Method
Proving that your building’s simulated EPI is lower than or equal to the benchmark EPI defined by the code.
Need help modeling your building? Visit DesignBuilder for ECBC-compliant simulation tools.
Rating Systems Based on EPI
Organizations like the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) in India provide EPI-based star ratings for:
-
🏢 Office buildings
-
🏥 Hospitals
-
🛍️ Shopping malls
These ratings promote transparency, encourage efficiency investments, and help you qualify for government incentives and green loans.
Explore BEE’s building rating directory at beeindia.gov.in/content/building.
EPI vs. Environmental Performance Index (Also Abbreviated as EPI)
⚠️ Don’t confuse the Energy Performance Index (building-level) with the Environmental Performance Index (national-level).
| Metric | Scope | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Performance Index | Individual buildings | Annual energy consumption |
| Environmental Performance Index | Countries | Environmental health & sustainability |
Check out the latest Environmental Performance Index rankings by Yale University at epi.yale.edu.
Conclusion: Why Energy Performance Index Matters
The Energy Performance Index is more than just a metric—it’s a roadmap for creating sustainable, cost-effective, and code-compliant buildings. Whether you’re an architect, facility manager, or developer, mastering EPI helps future-proof your assets in an increasingly energy-conscious world.